what are the causes,and types,
what are the symptoms, and treatment
Breast cancer is a form of cancer that originates from the breast tissue. It is one of the most common types of cancer in women, but it can also occur in men.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
The exact cause of breast cancer is still unknown,
but certain factors can increase a person’s risk. These include
- age,
-family history,
- lifestyle,
-certain medical conditions.
The stages of breast cancer generally range from 0 to IV, with 0 being the earliest stage of the disease. The stages indicate the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Common symptoms of breast cancer include
-a lump in the breast,
-changes to the breast skin or nipples,
- discharge from the nipples.
Treatment for breast cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer,
- but may include surgery,
- radiation,
- hormone therapy, and chemotherapy.
Medications used to treat breast cancer include
-hormonal therapy,
-chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
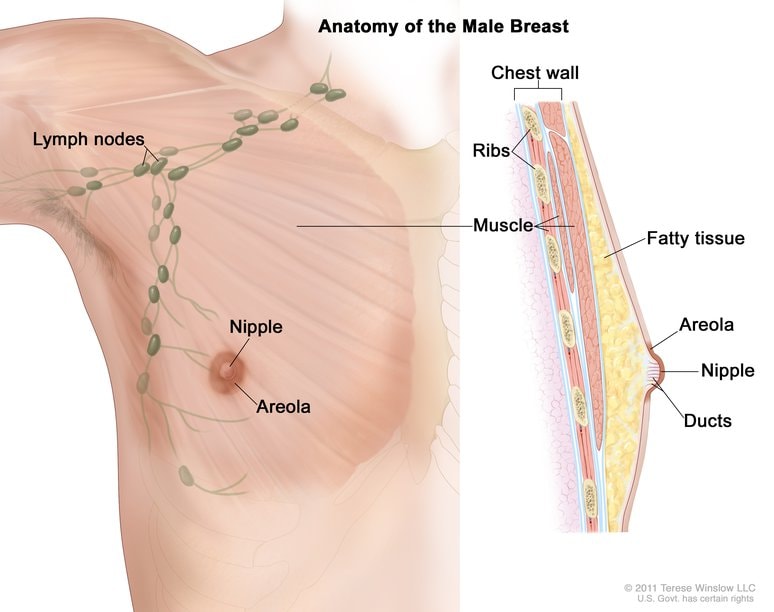
Breast Cancer in Men
Although it is rare, men can get breast cancer. Learn about symptoms of breast cancer in men and things that may increase your risk.
Breast cancer is most often found in women, but men can get breast cancer too. About 1 out of every 100 breast cancers diagnosed in the United States is found in a man.
The most common kinds of breast cancer in men are the same kinds in women—
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a breast disease that may lead to invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts, and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
What Are the Symptoms?
The most common symptoms of breast cancer in men are—
- A lump or swelling in the breast.
- Redness or flaky skin in the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Nipple discharge.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
These symptoms can happen with other conditions that are not cancer. If you have any symptoms or changes, see your doctor right away.
What Are the Risk Factors?
Several factors can increase a man’s chance of getting breast cancer. Having risk factors does not mean you will get breast cancer.
- Getting older. The risk for breast cancer increases with age. Most breast cancers are found after age 50.
- Genetic mutations. Inherited changes (mutations) in certain genes, , increase breast cancer risk.
- Family history of breast cancer. A man’s risk for breast cancer is higher if a close family member has had breast cancer.
- Radiation therapy treatment. Men who had radiation therapy to the chest have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Hormone therapy treatment. Drugs containing estrogen (a hormone that helps develop and maintain female sex characteristics), which were used to treat prostate cancer in the past, increase men’s breast cancer risk.
- Klinefelter syndrome. is a rare genetic condition in which a male has an extra X chromosome. This can lead to the body making higher levels of estrogen and lower levels of androgens (hormones that help develop and maintain male sex characteristics).
- Certain conditions that affect the testicles. Injury to, swelling in, or surgery to remove the testicles can increase breast cancer risk.
- Liver disease. Cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver can lower androgen levels and raise estrogen levels in men, increasing the risk of breast cancer.
- Overweight and obesity. Older men who are overweight or have obesity have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than men at a normal weight.